Reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions is essential in the fight against climate change. Carbon offsetting adds to the challenges of reducing emissions by removing emissions from the atmosphere that cannot be avoided now.
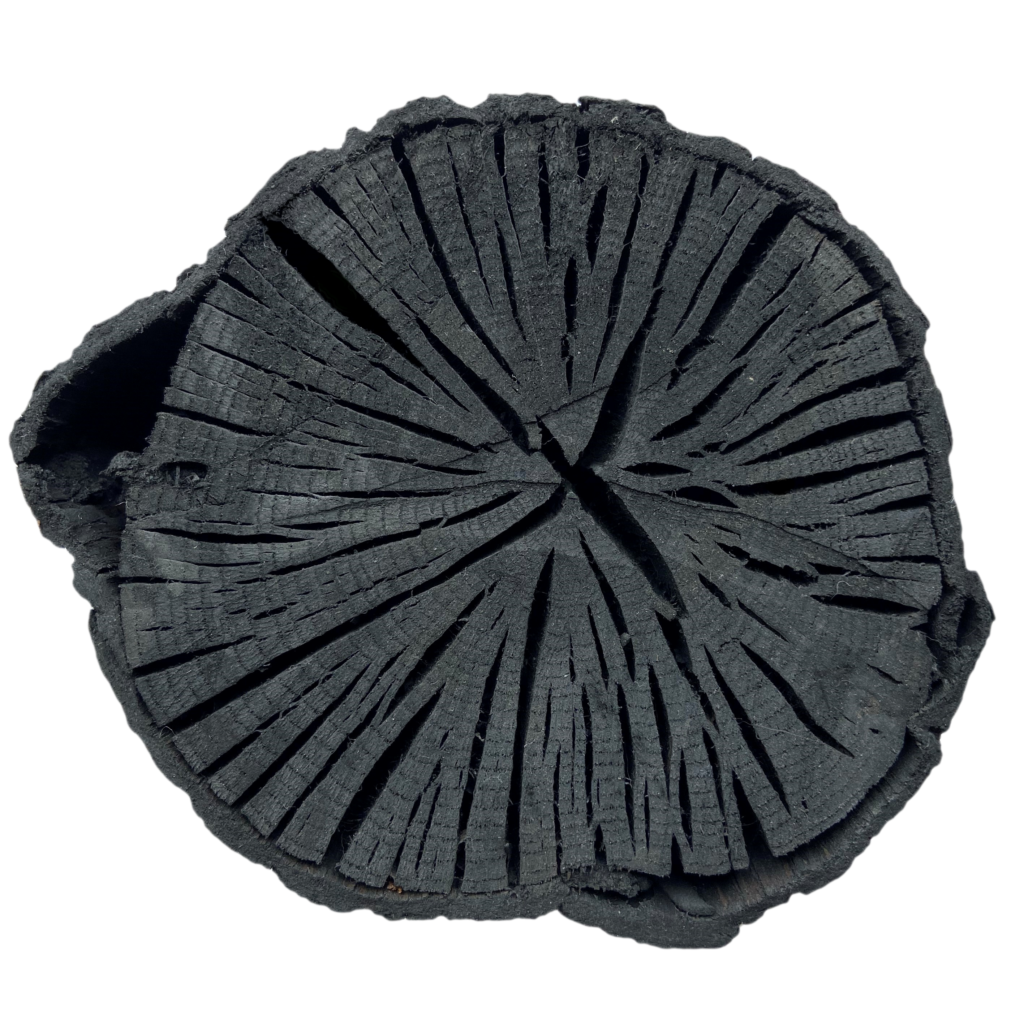

Pyrolysis stabilizes the carbon contained in this piece of oak in a highly stable form. Charcoal deposits have been found in Belgian, American and Brazilian soils, thousands of years old. This makes biochar an excellent material for carbon offsetting.
In the years to come, CO2 will have to be removed from the atmosphere. It is not enough to reduce emissions, and we must also sequester CO2. This article explains how carbon offsetting can be used to reduce the effects of climate change.
How much carbon do we need to offset?
Each year, global CO2 emissions reach around ten gigatonnes per year. In 2020, there was a slight drop due to the pandemic, but emissions are expected to quickly recover to pre-crisis levels. To reduce the effects of climate change, at least 6 Gt of carbon must be removed from the atmosphere each year.
It is possible to calculate the amount of GHGs emitted by different companies or individuals. This quantity of GHGs emitted into the atmosphere has, in the long term, effects in particular on the climate, we speak of carbon footprint. The more GHGs are emitted, the higher the carbon footprint will be.
Why do we need to offset carbon emissions?
How can we store carbon permanently?
What role does Carbon Centric play?
What is a carbon sink?
Biochar is a product derived from pyrolyzed organic matter with a high concentration of carbon, which gives it a potential for carbon offsetting as well as numerous technical applications. Prior to its physical incorporation in a medium preventing it from oxidizing, biochar has a significant carbon offset potential.
This carbon storage is not yet effective. It is only following its application in the binder that the actual storage takes effect. A carbon sink is then created. A carbon sink is a place where carbon is stored to prevent it from going into the atmosphere as CO2, which is a greenhouse gas (GHG). Carbon sinks have a real environmental value since they allow, on their scale, to reduce the quantity of CO2 in the atmosphere, which is one of the most critical challenges of our current society.
Carbon credits
Carbon credits can be issued to finance the creation of these sinks. Thus, companies, individuals or communities can buy carbon sinks to participate in the effort to reduce the concentration of atmospheric GHGs. Humanity aims to achieve net zero GHG emissions as soon as possible. This is called the NET ZERO goal. It is essential to understand that this is not obtaining a right to pollute but the need to reduce GHG emissions to remove what has already been emitted.
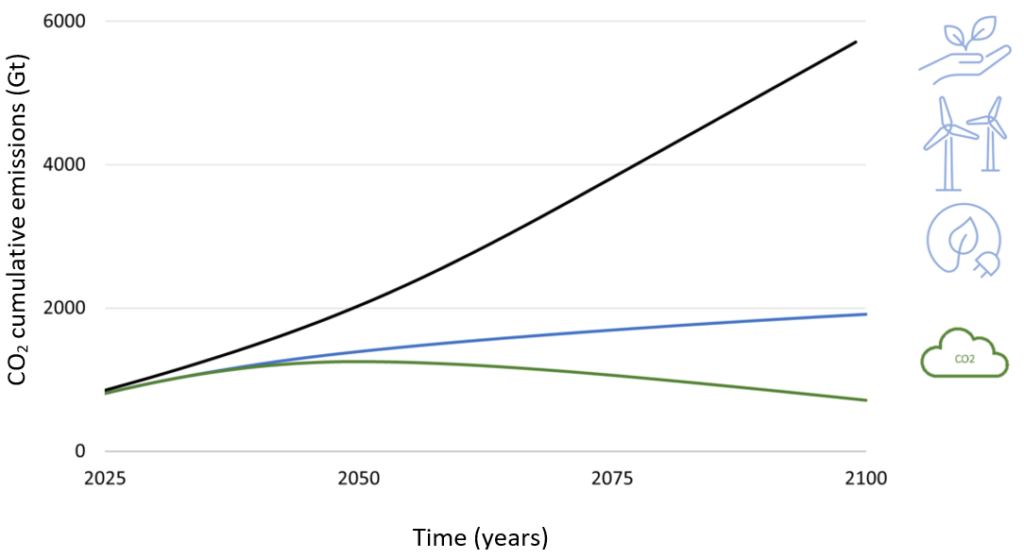
The cumulative CO2 emissions of three different scenarios. In black, the status quo scenario without reduction of CO2 emissions. In blue, significant and rapid emission reductions with traditional mitigation technologies. In green, reducing emissions combined with carbon offsetting is the only way to reduce the amount of carbon in the atmosphere. Source : MCC
How much is carbon offset needed?
Any approach to reducing your carbon footprint must start with an emissions reduction plan. Once the project is implemented, it is unlikely that the emissions of the company or the individual will be zero. It is then possible to compensate for the difference by having zero CO2 emissions.
There are different forms of offsetting emissions. All go through the creation of carbon sinks, which, as their name suggests, will store carbon. For example: planting trees during reforestation or afforestation projects. But also the “direct air capture” method to capture atmospheric CO2 to inject it into the subsoil, as well as biochar. These are the main current methods for creating carbon sinks.
Not all of them have the same impact on the environment, store carbon in the same way and do not consume the same amount of energy. The use of biochar is the one that meets the most criteria. Biochar stores carbon for long periods of time, emits energy that can be reused during its production, is a natural product, and if applied to the soil has beneficial agronomic properties for carbon, water retention and soil life.
| Biochar | Trees extract CO2 from the atmosphere. Thanks to pyrolysis, the carbon stored in plants can be fixed in the ground, concrete or buildings in the long term. Heat and electricity are also generated during the production of biochar. |
| Aforestation and reforestation | Trees extract CO2 from the atmosphere. Carbon can be bound in the medium or long term through the material use of biomass. If biomass is left in place, it will absorb less carbon over time. |
| Increasing organic matter in soils | Different techniques can be used to increase the soil’s organic matter (and therefore carbon) content. Methods such as manure spreading, tillage, mixed cropping and agroforestry can improve soil carbon content.niques peuvent être utilisées pour augmenter la teneur en matière organique (et donc en carbone) du sol. Des méthodes telles que l’épandage de fumier, le travail du sol, les cultures mixtes et l’agroforesterie peuvent augmenter la teneur en carbone du sol. |
| Forced weathering | Rock (Basalt) is crushed and exposed to natural weathering and mineralization. The weathering process removes CO2 from the atmosphere, and the carbon is sequestered as carbonate rock. |
| Bioenergy and carbon storage | In this process, carbon emissions from bioenergy plants are captured before being emitted into the atmosphere and pumped underground. |
| Direct CO2 capture | CO2 from the air is extracted using filters or by a chemical process and the carbon captured is stored underground. There are currently very few examples of this technology in operation. |
Verified and authenticated carbon offsets
Traceability along the value chain is essential. It is necessary to know the source of the organic matter used, the place of transformation and the place of the creation of the carbon sink. Once the credit has been issued, it is also essential to ensure its authenticity. To ensure total transparency and security on the sustainability of our supply and that of carbon credits. We have developed a blockchain-based traceability system.
Thanks to carbon credits from biochar, a company will be able to implement solutions not only to stop emitting CO2, but it will also be able to finance the creation of carbon sinks to remove the rest of its emissions. This company’s net emissions will be neutral thanks to our Carbon Removal Certificate.
The projects carried out and supported by Carbon Centric are carefully selected. They have a real benefit for the environment, and they come from sustainably sourced organic matter. The key to a good biochar carbon sink is, beyond its ability to store carbon, the responsible sourcing of organic matter.
Did you know it?
It is through our local supply chain that we can ensure traceability and accurately calculate the carbon storage value of our biochar. Carbon Centric biochar is made from wood grown in local, sustainably managed French forests. The vast majority of our wood comes from cleared timber that is removed from the forest to promote the growth of older trees. We also use wood waste from surrounding sawmills.
Agronomic biochar for resilient crops
The financing of biochar projects makes it possible to subsidize the use of biochar for its agronomic properties to farmers. Indeed, the income generated by carbon-carbon emissions goes back to the farmers. Biochar is used to make crops more resilient to climate change. Indeed, farmers are on the front line in the face of the vagaries of the climate. Healthier and more resilient crops allow farmers to reduce the passage of machinery, crop inputs and treatments. This beneficial social impact is possible thanks to financing projects by Carbon Centric carbon removal certificates.
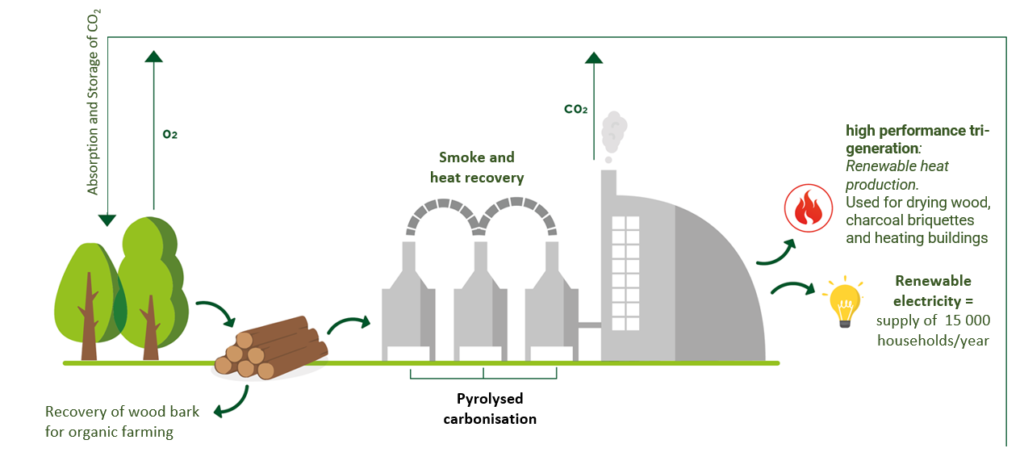
Thanks to systems with such efficiencies and by producing electricities for nearly 15,000 households, Carbon Centric’s biochar production is considered as carbon negative.
Let’s work together for a single goal: NET ZERO
Carbon sinks from biochar are part of a set of solutions that must be implemented simultaneously to achieve our objective of limiting climate change. The Paris Agreements, signed at COP 21, set ambitious but necessary targets for the concentration of CO21 in the atmosphere in order to limit global warming to 2°C. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), this goal can only be achieved if we achieve global carbon neutrality and some of the previously emitted emissions are removed. Although the task seems colossal, it is by combining projects such as the carbon sinks of biochar that we will achieve it.
Carbon offsetting with Carbon Centric
For each ton of CO2 equivalent stored, Carbon Removal Certificates are issued and sold to companies or individuals wishing to offset their residual emissions. When purchasing Carbon Centric Carbon Removal Certificates, the value of the carbon sink is transferred to the creator of the sink, usually farmers who can thus benefit from the agronomic effects of the Carbon Centric biochar.
If you wish to participate in the effort, whether through your project to create carbon sinks or by financing other actions, the Carbon Centric teams are at your disposal to support you and guide you towards the NET objective. ZERO. Contact us, we will answer you as soon as possible.
Article par Emil Soler-My
Emil is an expert in carbon trading and energy markets. Since graduating, he has led business development projects in France, Germany and the United States.

Sources
1. ICOS. Data supplement to the Global Carbon Budget 2021. https://www.icos-cp.eu/science-and-impact/global-carbon-budget/2021 (2021).


